CSIP: PRELIMS BOOSTER SERIES- 159 INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership)
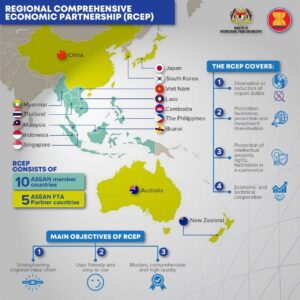
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a substantial trade agreement that has been in negotiation since 2012. It brings together the 10 ASEAN member states and six Free Trade Agreement (FTA) partners.
Membership:
– ASEAN Members: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia.
– FTA Partners: Australia, China, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea.
Objectives:
– RCEP aims to boost economic growth, foster equitable development, and promote economic cooperation and integration in the region. It covers trade in goods and services, investment, intellectual property, and dispute resolution.
Background:
– RCEP builds upon existing ASEAN+1 FTAs with the goal of strengthening economic linkages and minimizing development gaps.
India’s Exit:
– India withdrew in 2019 due to concerns about unfavourable trade balances, particularly with China. India also sought an auto-trigger mechanism to deal with rising imports, which was not accepted by other RCEP nations.
Issues:
– Concerns about trade imbalances.
– India’s trade deficit with China.
– Protection of domestic industries, such as dairy, textiles, steel, and agriculture.
– Lack of consensus on rules of origin.
Way Forward
– Strengthen existing trade agreements.
– Market Indian products effectively.
– Diversify exports into growing regions.
– Implement economic reforms.
– Promote exports with a targeted approach.
– Maintain external integration strategies to explore new opportunities.