CSIP: PRELIMS BOOSTER SERIES -658 INDEX AND REPORTS
GLOBAL HEPATITIS REPORT
Why in News?
According to the World Health Organisation’s (WHO’s) Global Hepatitis Report 2024, India has among the highest burdens of viral hepatitis — tied with tuberculosis (TB) as the second largest infectious killer globally — in the world. Covid-19 was the number one infectious killer, according to the report which used data from 2022.
What is Global Hepatitis Report’s Findings?
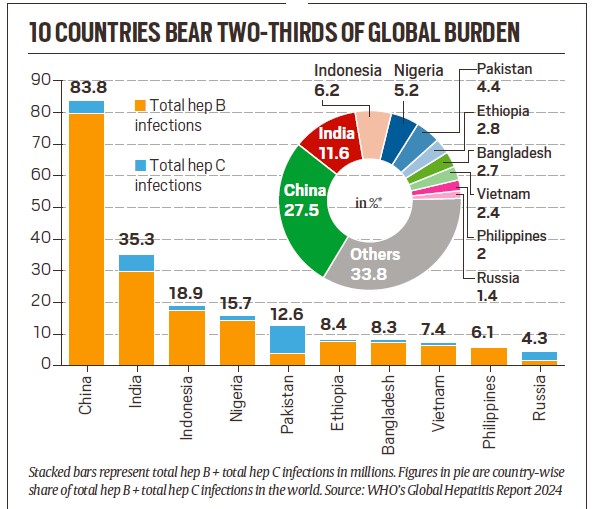
- India has the world’s second highest prevalence of viral hepatitis cases, accounting for over 11% of the global burden, the report found.
- Of the 50 million people living with hep C in the world, India accounted for 5.5 million cases, just behind Pakistan’s8 million cases. The diagnosis of viral hepatitis also remained abysmally low. According to the report, only 2.4% hep B cases and about 28% hep C cases were diagnosed.
- Dr Sarin, however, said that India’s hep B cases are driven up by mother-to-child transmission.
- With regard to hep C, the WHO report says that India is one of 10 countries where 80% infections are among injection drug users.
What is Hepatitis?
- Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. It causes liver diseases, including acute and chronic infections, liver failure, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- According to WHO, there are five main strains of the hepatitis virus, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E.
- The Hepatitis A virus causes an infectious liver disease. It is acute, and most symptoms are not recognised, particularly in young people. The symptoms are vomiting, nausea, fever, severe stomach pain, jaundice, and weakness.
- Hepatitis B is a contagious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus. It is transmitted through flat, exhausted wounds and contact with an infectious body’s blood, saliva, or secretions.
- The Hepatitis C virus causes an infection of the liver. This can be transmitted through infected needles, at birth, through an infected person’s body fluids, or by having sex with several partners, particularly HIV-infected people.
- Hepatitis D is one of several serious liver illnesses caused by the Hepatitis D virus. It spreads through infected blood or wounds and may occur in association with Hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis E: This is a waterborne disease caused by a virus. It could be spread through food, water, or tainted blood. It could be acute or persistent.
- Hepatitis B can be prevented through
- Hepatitis C is curable with medicines.
- The Hepatitis B vaccine is offered to children under the Universal Immunisation Programme in India, whereas the government’s National viral hepatitis control programme also offers the vaccine to high-risk adults, such as healthcare workers.
- Havisure: It is India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine.

