CSIP: PRELIMS BOOSTER SERIES -667 WORLD GEOGRAPHY
ARAL SEA
Why in News?
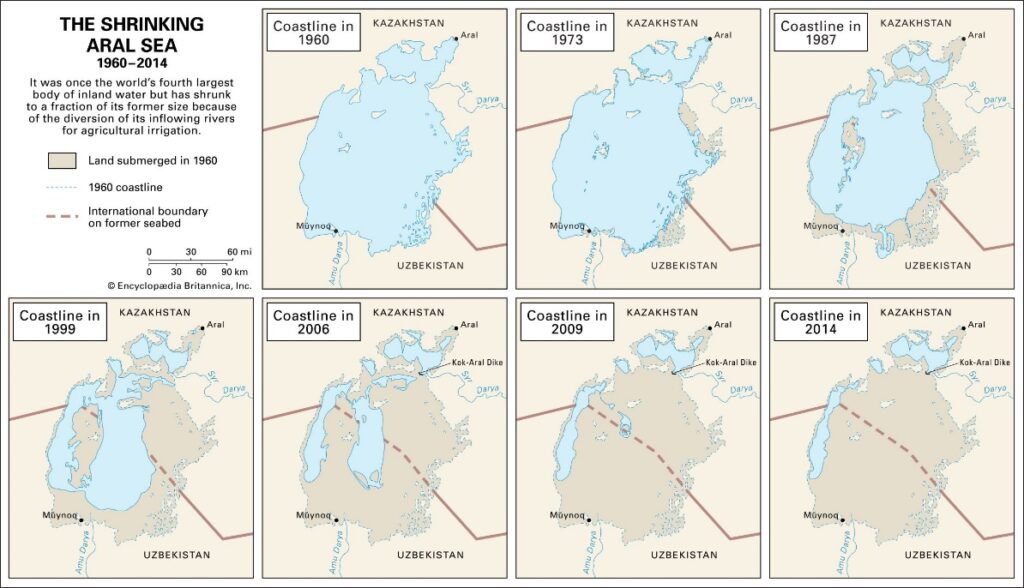
The Aral Sea, the world’s fourth-largest lake until the early 1960s, dried up after that decade in Soviet Central Asia and became a byword for environmental disaster later, almost on the lines of the Chernobyl nuclear disaster. Now, a new study has found that the desert which emerged due to the drying up of the lake, has made Central Asia a much dustier place. Not only is the dust more hazardous than normal dust but it will also have impacts on global climate, though more studies are needed to ascertain that.
What is Aral Sea?
- It is also known as Orol Dengizi (Uzbek) or Aral Tengizi (Kazakh).
- It was the fourth largest inland lake in Central Asia.
- After the 1960s, It dried up and got converted into desert.
- Aralkum Desert It is smaller than neighbouring deserts: Karakum (350,000 sq km) in Turkmenistan and Kyzylkum (300,000 sq km) in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan.
- Despite its size, the Aralkum Desert is a major human-made dust source
- It lies across the border between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, extending from the south to the north.
- The area has a desert-continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Major rivers: The Amu Darya, known as Oxus in ancient times, and the Syr Darya, also called Jaxartes. They flowed from the Pamir and Tien Shan Mountain ranges, respectively.